THE UNIVERSE - PART 4
MILKY WAY GALAXY
1. Milky Way looks like a stream of milk across the sky. Some of the important features are given below.
1. Milky Way looks like a stream of milk across the sky. Some of the important features are given below.
Shape & Size
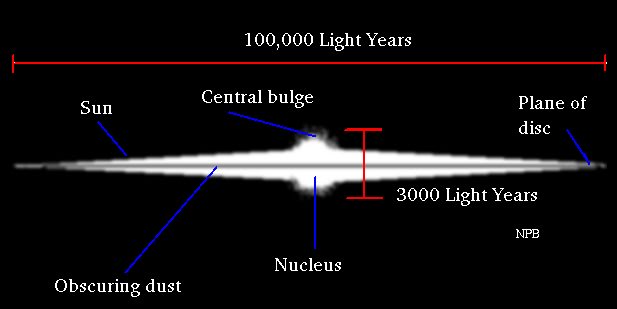
• Milky Way is thick at the centre and thin at the edges. The diameter of the disc is 105 light years.
• The thickness of the Milky Way varies from 5000 light years at the centre to 1000 light years at the position of the Sun and to 500 light years at the edges.
• The Sun is at a distance of about 27000 light years from the galactic centre.
Interstellar matter
• The interstellar space in the Milky Way is filled with dust and gases called inter stellar matter.
• It is found that about 90% of the matter is in the form of hydrogen.
Clusters
• Groups of stars held by mutual gravitational force in the galaxy are called star clusters.
• A star cluster moves as a whole in the galaxy.
• A group of 100 to 1000 stars is called galactic cluster.
• A group of about 10000 stars is called globular cluster.
Rotation
• The galaxy is rotating about an axis passing through its centre.
• All the stars in the Milky Way revolve around the centre and complete one revolution in about 300 million years.
• The Sun, one of the many stars revolves around the centre with a velocity of 250 km/s and its period of revolution is about 220 million years.
Mass
• The mass of the Milky Way is estimated to be 3 × 1041 kg.
ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE
1. Big Bang Theory :
• According to the big bang theory all matter in the universe was concentrated as a single extremely dense and hot fire ball.
• An explosion occurred about 20 billion years ago and the matter was broken into pieces, thrown off in all directions in the form of galaxies.
• Due to continuous movement more and more galaxies will go beyond the boundary and will be lost.
• Consequently, the number of galaxies per unit volume will go on decreasing and ultimately, we will have an empty universe.
2. Pulsating Theory :
• Some astronomers believe that if the total mass of the universe is more than a certain value, the expansion of the galaxies would be stopped by the gravitational pull.
• Then the universe may again contract. After it has contracted to a certain critical size, an explosion again occurs. The expansion and contraction repeat after every eight billion years.
• Thus we may have alternate expansion and contraction giving rise to a pulsating universe.
3. Steady state Theory :
• According to this theory, new galaxies are continuously created out of empty space to fill up the gap caused by the galaxies which escape from the observable part of the universe.
• This theory, therefore suggests that the universe has always appeared as it does today and the rate of expansion has been the same in the past and will remain the same in future.
• So a steady state has been achieved so that the total number of galaxies in the universe remains constant.








No comments:
Post a Comment